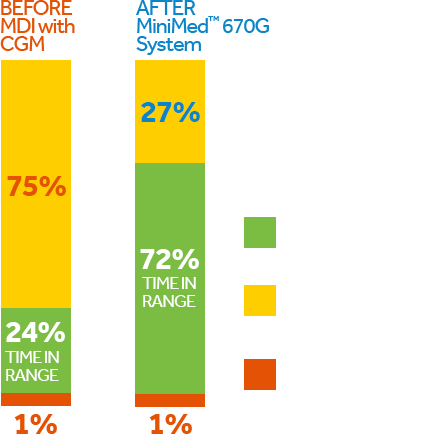
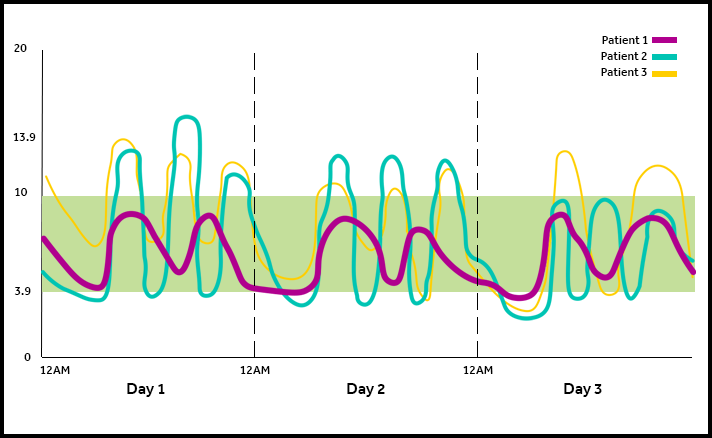
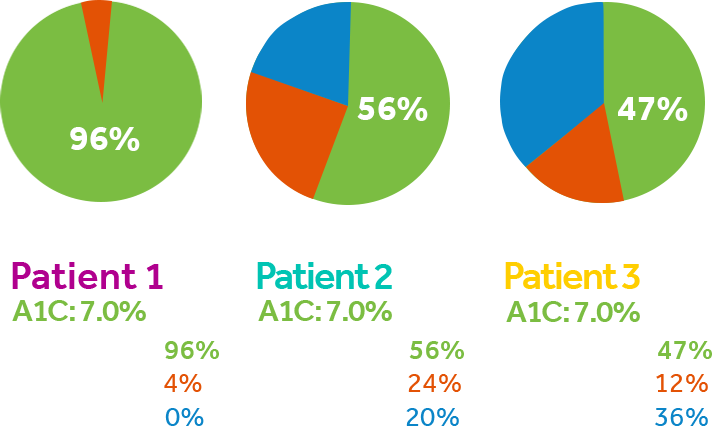
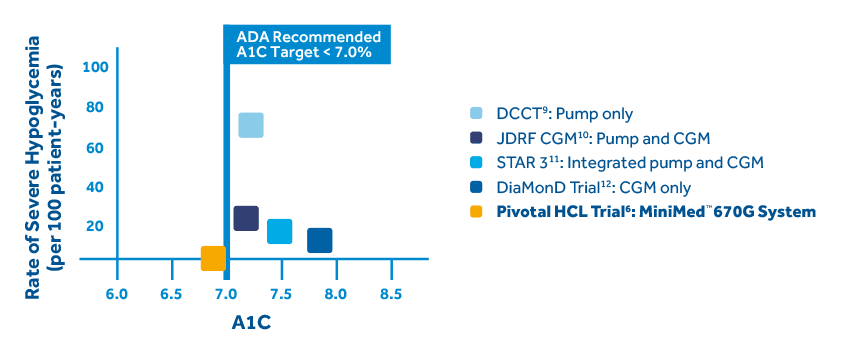
The MiniMed™ 670G system offers SmartGuard™ Auto Mode™, the only technology that mimics some of the functions of a healthy pancreas by providing two levels of insulin delivery for type one patients 7 years or older.
SmartGuard® AUTO MODE FEATURES:
- Automatically adjusts your basal (background) insulin every five minutes based on your CGM readings.*,#
- Helps keep your sugar levels in your target range for fewer lows and highs — day and night.*,#,1
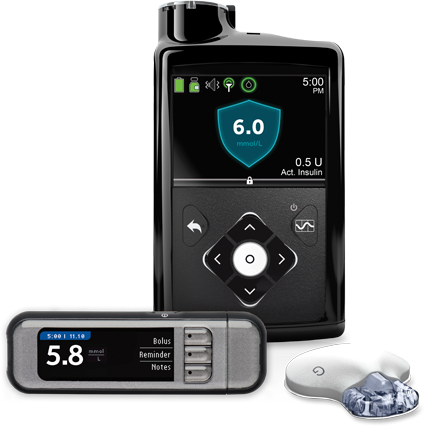
The MiniMed™ 670g system.
| Water Resistance | Waterproof pump, protected against the effects of being underwater to a depth of up to 12 feet (3.6 meters) for up to 24 hours. |
|---|---|
| Sizing | The pump dimensions in inches are approximately 2.1 width x 3.78 length x 0.96 depth. The weight of the pump is approximately 3 ounces. |
| Environmental Conditions | The MiniMed™ 670G insulin pump system is designed to withstand most conditions encountered in your daily life. Pump storage temperature range is from -4 °F (-20 °C) to 122 °F (50 °C). Air pressure range is from 700 hPa to 1060 hPa (10.2 psi to 15.4 psi) |
| Pump Memory | At any time the user can review 90 days of pump history |
| Compatible Infusion Sets | Medtronic Diabetes provides a variety of infusion sets to fit your needs. |
| Guardian™ Link 3 Transmitter | Used with your pump for Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM). A device that connects to a glucose sensor. The transmitter collects data measured by the sensor and wirelessly sends this data to monitoring devices. |
| Bolus™ Speed Options |
|
| Bolus™ Programming Increments |
|
| Altitude Range |
|
| Backlight |
|
| Basal Delivery Rate Range | 0 to 35 units per hour or the Max Basal Rate amount, whichever is lower. |
| Guardian™ Sensor 3 | Used with your pump for CGM. The sensor is a small part of the continuous glucose monitoring system that you insert just below your skin to measure glucose levels in your interstitial fluid. |
| Carelink™ USB | Used to upload system data to the diabetes management software using a USB port on your computer. |
| One-press Serter | The serter is used as an aid for inserting the sensor. It is indicated for single-patient use and is not intended for multiple patient use. |
| Battery & Power | The pump requires one new AA (1.5 V) battery. For best results, use a new AA lithium (FR6) battery. The pump also accepts an AA alkaline (LR6) or a fully charged AA NiMH (HR6) nickel-metal hydride rechargeable battery. |
| Reservoir | Medtronic reservoir MMT-332A, 3.0 ml (300-unit) |
| CONTOUR®NEXT LINK 2.4 Glucose Meter | The MiniMed™ 670G system comes with a compatible meter. It wirelessly connects to your pump, allowing you to send BG meter readings to your pump. |